
Another Arctic blast will surge south across the northern Plains Thursday night, crossing the Midwest and reaching the Gulf Coast Friday night. Confidence continues to increase for significant heavy snow across much of the Southern Appalachians, Carolinas, and southern Mid-Atlantic Friday into Sunday. Read More >
Western and Central Wyoming
Weather Forecast Office
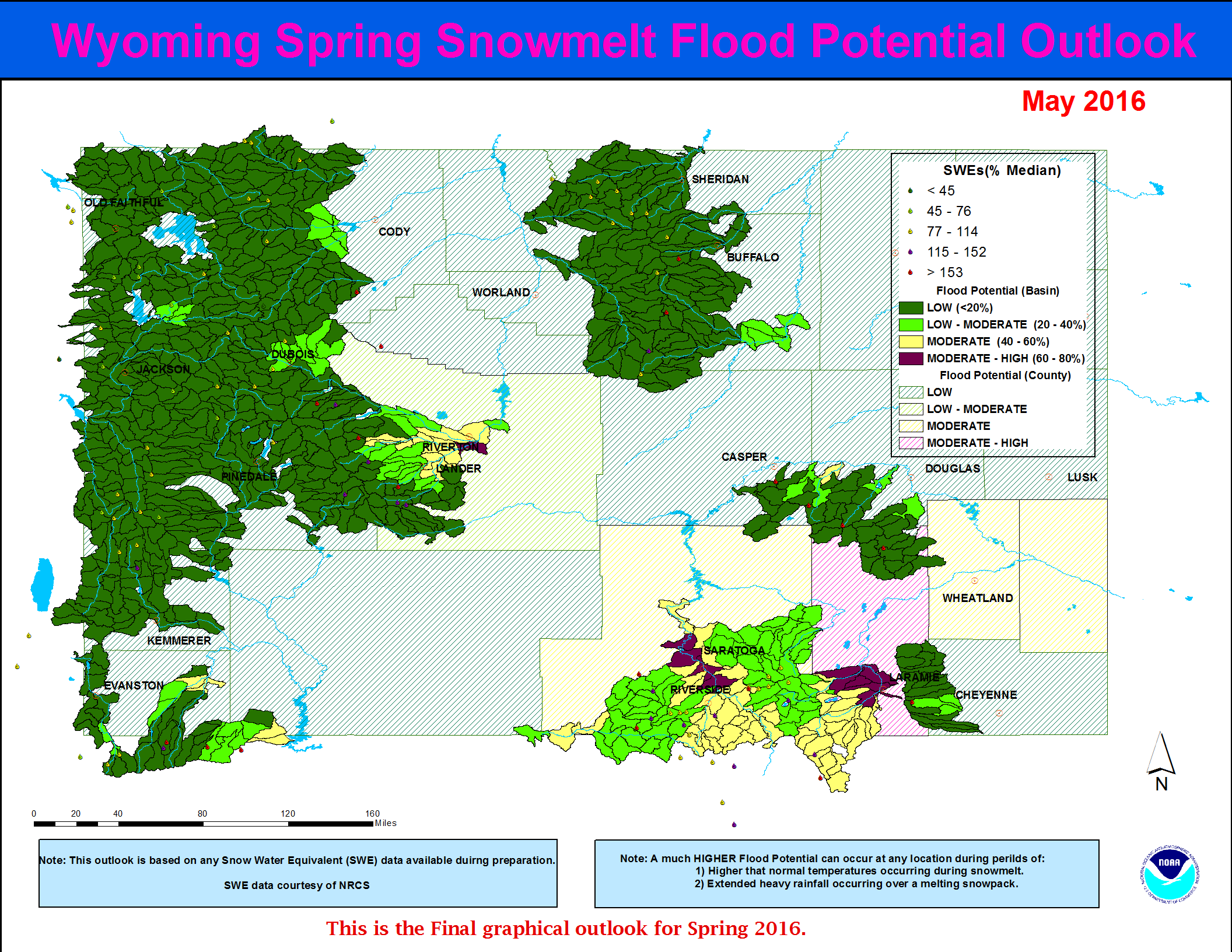
Mountain snowpack and associated snow water equivalents (SWEs) across most of Wyoming were generally near to slightly above average by late February. SWEs at the peak snowmelt runoff elevations (8,500’ – 10,000’) were the highest across the Little Snake and Upper North Platte Basins at 105 to 115 percent of median. The Upper Yellowstone and Tongue Drainages had SWEs at 85 to near 95 percent of median at the peak snowmelt runoff elevations.
This outlook is based on various diverse hydrological factors such as snow water equivalents (SWEs) in the mountain snowpack, basin morphology (i.e. how basins respond to snowmelt runoff), antecedent soil moisture, biological/physical factors (bark beetle kill/spruce blight///fire burn scars), low elevation snow depths, and likely temperature and precipitation trends during late spring/early summer.
…Moderate potential for snowmelt runoff flooding is forecasted along the lower portions of the Upper North Platte River Basin (near Saratoga) and along the lower portions of the Laramie Watershed (near Laramie)…
…All other of headwater basins across Wyoming can expect a generally Low potential for flooding due to springtime snowmelt runoff...
The current Wyoming Spring 2019 Snowmelt Runoff Flood Potential Outlook graphic:
Forecasts
Severe Weather
Forecast Discussion
User Defined Forecast
Fire Weather
Activity Planner
Hourly Forecasts
Snow and Avalanche
Aviation Weather Decision Support
Hydrology
SnoTel Page
Rivers and Lakes
Weather Safety
Preparedness
SkyWarn
StormReady
NOAA Weather Radio
US Dept of Commerce
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
National Weather Service
Western and Central Wyoming
12744 West U.S. Hwy 26
Riverton, WY 82501
307-857-3898
Comments? Questions? Please Contact Us.

