
A storm system will produce severe thunderstorms over and near Louisiana, and heavy to excessive rainfall from the Southern Plains through the Ohio River Valley today. A strong weather system will bring the potential for flash flooding, severe thunderstorms, strong to locally damaging non-thunderstorm winds, and high elevation snow to the Hawaiian Islands through Friday. Read More >

2017 Solar Eclipse
Summary and Eclipse Path | Climatology | Forecast | What is an Eclipse? | Eclipse Safety
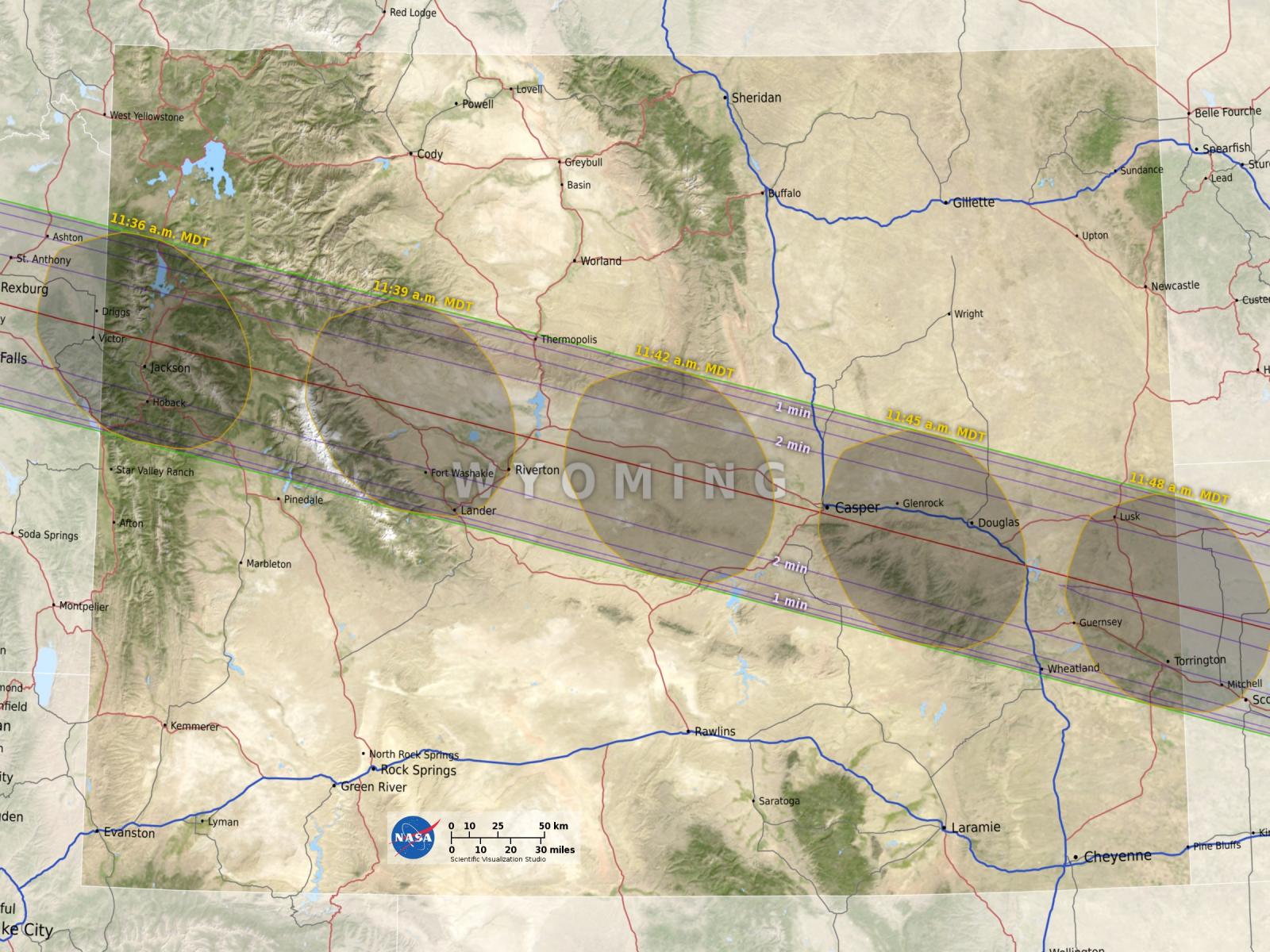
A total solar eclipse will track from the Pacific coast to the Atlantic. The shadow of the moon will begin over Oregon and move east to Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Nebraska, Kansas, Missouri, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Georgia, and South Carolina. Totality will begin over the US in Newport, OR at 11:16 MDT and will end near Charleston, SC at 12:48 MDT. A partial solar eclipse will be viewable over the rest of the US. Totality will track directly across Wyoming and Nebraska. At the center of totality the moon will block out the sun completely for approximately 2 minutes 40 seconds. Totality time will decrease the further you are away from the center of totality. An event of this magnitude will not occur again until 2045.
Blue Line: Center of Totality Red Lines: Northern and Southern Boundaries of Totality |
| Wyoming Eclipse Map - Path and Times | ||
 |
 |
|
|
Click on Images to Enlarge |
||
Sunshine over most of Wyoming in the summer is a common occurrence, about 75% of the time during the summer. A minimum in cloudiness occurs in the late summer especially during the morning hours. Cumulus clouds develop almost every day contributing to partly to mostly cloudy afternoons. If you are looking for the odds of seeing the solar eclipse Wyoming the odds are in your favor. The solar eclipse will reach totality from 11:34 to 11:48 AM lasting for just over 2 minutes.
 |
 |
|
| Click on Images to Enlarge | ||
 |
 |
|
| Click on Images to Enlarge | ||
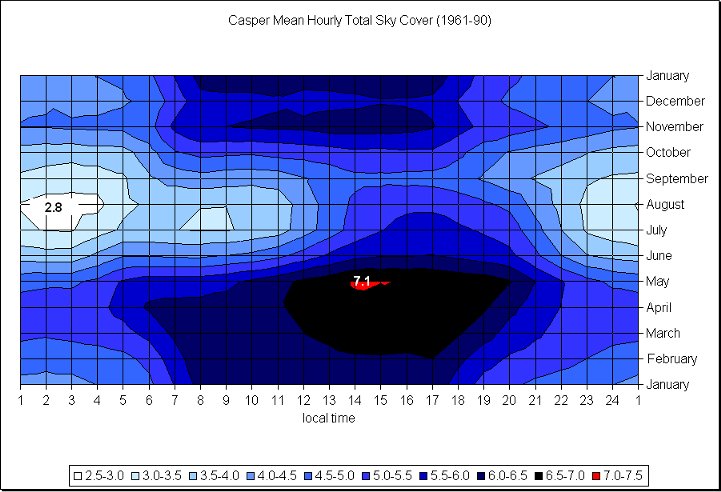
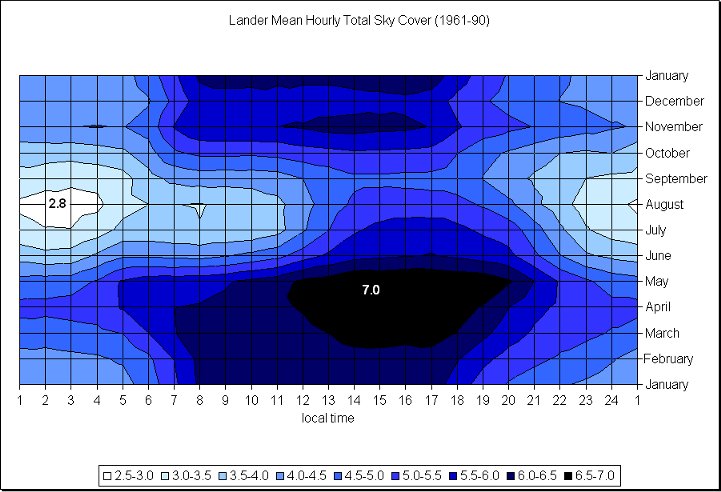
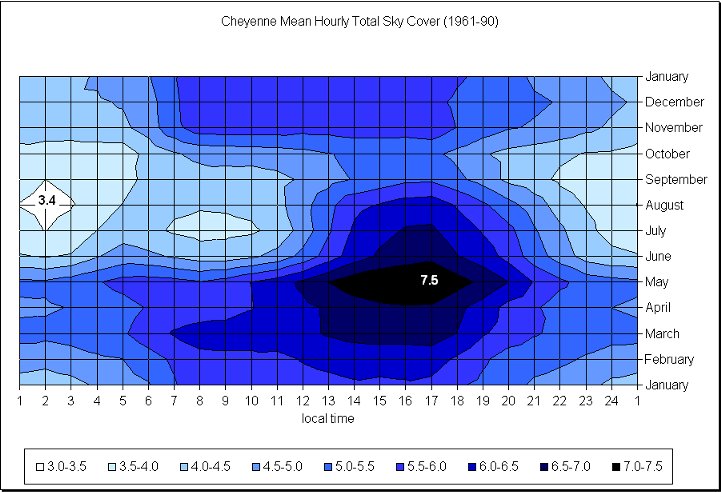
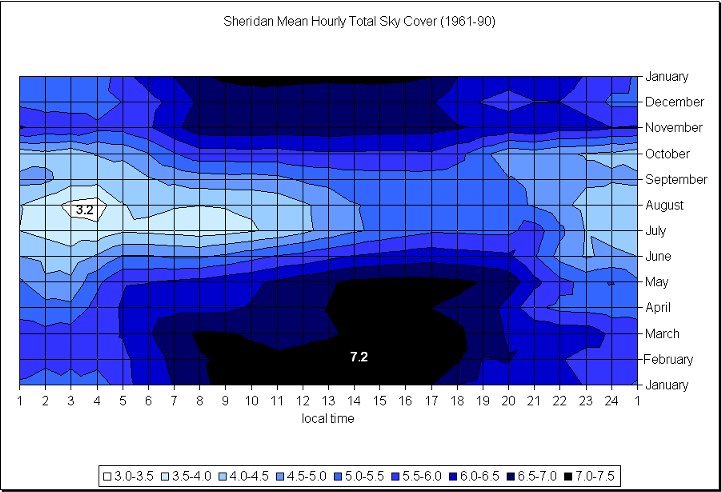
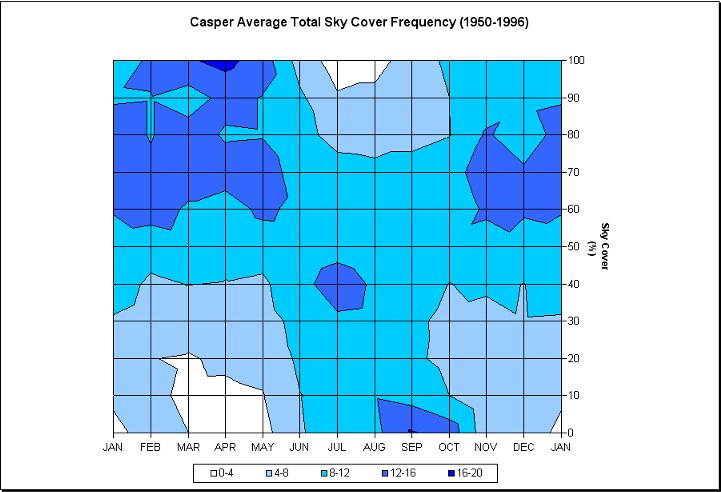
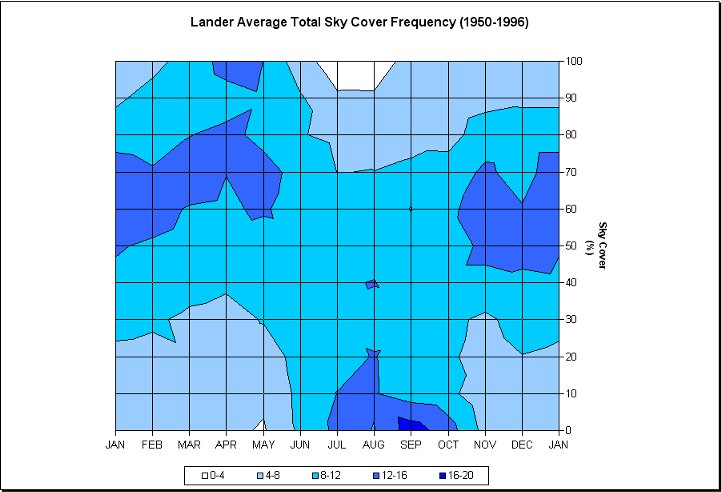
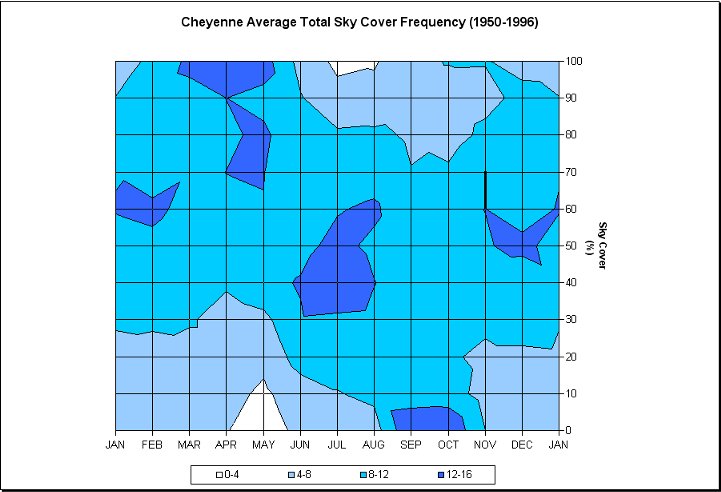
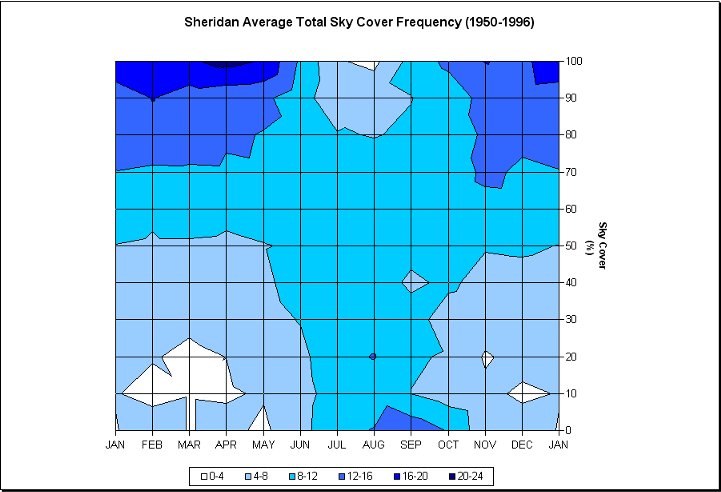
Photo credit: Wyoming Climate Atlas, University of Wyoming
 |
 |
Over the last 3 years past satellite shows little cloud cover over Wyoming and Nebraska. Visible satellite images taken at 17Z (11:00 AM MDT). 2014 partly cloudy skies existed over Wyoming, and 2015 and 2016 had clear skies. In the summer the sun is not only visible a majority of the time, but also when the sun is most intense. Due to the elevation (most of Wyoming sits over 6,000 ft or 1,828 m) the sun's rays have less atmosphere to penetrate, thus eliminating the potential for haze, fog, and smoke contamination.
The data in these graphs is based on climatology and show the average cloud cover for the different cities. The charts show the possibility of what the cloud coverage amounts might be on August 21st, but are not actual forecasts. A forecast will be available as we approach the date of the Total Solar Eclipse.
Choose a forecast product type (temperature, wind, cloud cover, etc) and desired time from the menu/slider bars at the top of the map. The map will update automatically. Use your mouse to zoom into/pan around on the map.
National Weather Service forecasts are issued out to 7 days. Please check back for accurate forecasts near the eclipse date. The current forecasts are only for the next several days NOT the date of the eclipse (August 21).
An eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon move into alignment with each other. One of the bodies blocks the view of another and creates a shadow. There are 2 different types of eclipses: solar and lunar.
A lunar eclipse happens at nighttime and occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon creating a shadow on the Moon. These types of eclipses occur roughly 2 to 4 times per year. A lunar eclipse will generally last for a few hours.

Lunar eclipses seem to be more numerous than Solar Eclipses each year because, unlike a solar eclipse which only covers a narrow band of the earth, each lunar eclipse is visible from over half the Earth. Any given location on earth can have up to three lunar eclipses per year, but some years there may be none.
Solar eclipses, especially total solar eclipses, are a rare special to see. Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes in between the Earth and the Sun, putting the Earth into its shadow. Most calendar years have 2 to 4 solar eclipses. They seem rarer because each time a solar eclipse occurs it is visible over a different, narrow region of the earth. In 1935 there was a very rare occasion of 5 eclipses for the year. That will not happen again until 2206.

It is important to note that viewing a Solar Eclipse can be dangerous to your eyesight. Eclipse viewing safety is explained below.
Solar eclipses can be broken up into 3 categories: Partial, Total and Annular. A partial solar eclipse occurs when the moon does not completely block out the Sun. The Moon, Sun, and Earth do not form into a perfectly straight line, so only a portion of the sun is covered.
An annular eclipse occurs when the moon passes in front of the sun but due to the fact that the moon is sometimes further from the earth it appears too small to fully cover the disk of the sun. A bright “ring of fire” is visible around the moon. Annular eclipses, meaning “ring-shaped”, only occur during the New Moon phase, when the Sun and Earth are aligned on opposite sides of the moon, and the moon is near its farthest point from the Earth (apogee).
A total solar eclipse is the type we will experience on August 21, 2017. The Moon, Sun, and Earth will align allowing the moon to completely cover the sun. Only during the time of total blockage is it safe to look at the eclipse without any eye protection. The total blockage of the sun will only last for a few minutes before the Moon moves and the sun will begin to reappear.
A few interesting historical facts:
Community and social events are being held across the United States click here to find one across the US
Safety is a big concern when viewing a solar eclipse. You should NEVER look directly at the sun during an eclipse. Looking directly at the sun is only safe during the few minutes when the eclipse is at the totality. That will only occur in the very narrow path of about 60 to 70 miles wide from Oregon to South Carolina (see map above).
The only way to safely observe a partially eclipsed sun is through special solar filtered glasses. Homemade filters and ordinary sunglasses are not safe for looking at the Sun. There are several manufacturers of eclipse glasses to meet international standards.These glasses can be found at various online retailers and are generally inexpensive. Be sure to follow any packaging instructions and supervise children using solar glasses.
.jpg)
NASA Eclipse Safety Information
If you are looking for a DIY solar eclipse viewer a pinhole projector is a safe but indirect way to view a solar eclipse. You can make one large enough to fit over your head, or use a smaller box you can hold in your hands, such as a cereal box.
Other ways to view a solar eclipse include: